Can a Dual Nic Be Used for Two Seperate Excternal Private Hyperv Networks
Nosotros are reader supported and may receive a commission when you make purchases using the links on our site
Hyper-V Networking Guide
Hyper-V offers an easy fashion to implement virtualization. In this article, we explain the engineering science.

Virtualization is a well-established resources resource allotment method and the technology that implements information technology is very stable. The Hyper-V system is a product of Microsoft and integrates well with other Microsoft products – notably Windows. If y'all are just embarking on a Hyper-V project, you demand to get familiar with the terminology of virtualization and make a clear argument of objectives that you lot can translate into a verifiable plan.
The basics of Hyper-Five
The underlying technology of Hyper-V is easier to empathize if you accept experience in networking engineering science. Specifically, information technology helps if you understand Layer 2 and Layer 3 concepts. Equally an indicator, Layer 2 is concerned with MAC addresses and switches, and Layer 3 works with IP addresses and routers.
Approach Hyper-Five with new eyes. That means, don't assume if you have experience with other virtualization systems that Hyper-Five works the same as those other systems. Learn the methodologies of Hyper-V implementation from the ground up – don't skip steps and don't make assumptions.
Get Hyper-V operating at Layer two
The Hyper-V implementation has two elements – a Hyper-V server and a virtual machine (VM). These two elements need to communicate with each other across a network. Even if they are both operating on the same computer, the conventions of Hyper-V mean that these two components connect to each other through a switch. The doesn't necessarily hateful a physical switch on your network.
At this point, you are dealing with Layer 2, so you need your virtualization to be able to communicate with a switch. All VMs are continued to a virtual switch. For the fourth dimension being, nosotros will deal with VMs connecting to a virtual switch, which in turn connects to a physical switch. The server will connect directly to a physical switch.
Your Hyper-V management software and the virtual server will exist resident on a concrete server that runs either Windows Server or Windows x. So, you demand to brand sure that the Hyper-V system can communicate with the network interface on the physical server.
An important concept to sympathise is that the VM does not exist in the physical world. The physical server exists and communicates with real switches on behalf of the Hyper-V arrangement, as it does for all of the other network-reliant applications that it runs.
The Hyper-V virtual server is an application on the concrete server, so it has access to the network and to concrete switches. The virtual machine does non communicate with physical switches. It communicates with a Hyper-V virtual switch.
The Hyper-V virtual switch
The Hyper-Five virtual switch is really a relabeling of a network adapter. That network adapter cannot have two identities. So, one time it is assigned to a virtual switch, it has no other purpose and cannot exist accessed in whatsoever other way. The Hyper-5 virtual switch occupies the network adapter entirely.
In one case you assign a network adapter to a virtual switch identity, the operating system ceases to recognize that NIC as a network adapter. That means you won't see information technology listed as an adapter in the Network Connections folder in Windows Settings. And then, the procedures that you lot are used to using through the operating system to manage and conform adapters tin't be used for your virtual switch.
The Hyper-Five server can connect to a virtual switch. However, it can't use the same virtual switch that serves the VM, then it is a bit of a waste of time channeling the server to a virtual switch. That strategy would demand for you to prepare a network adapter on the concrete server and a virtual switch. That's unnecessary overhead. It is ameliorate to let the Hyper-V server communicate with a concrete switch through a network adapter and set up a separate network adapter as a virtual switch for the VMs to employ.
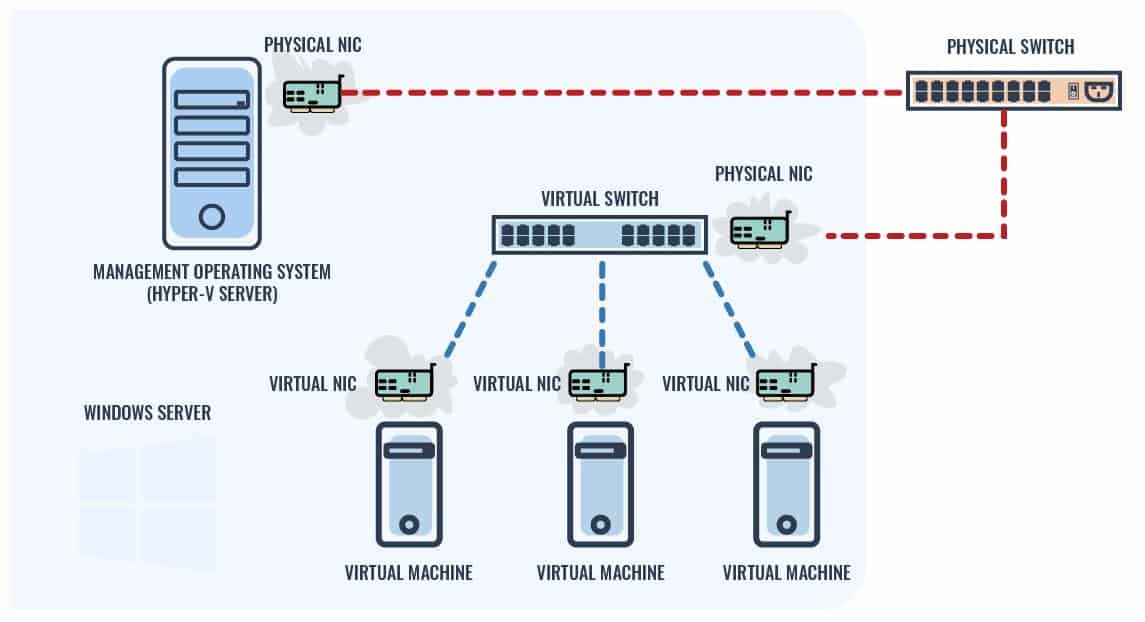
Substantially, this exercise requires a loopback from i adapter on the physical server out to a switch and back to another network adapter on the same server.
Here are some facts most virtual switches to go on in mind:
- Each VM connects to a virtual switch via a virtual NIC.
- Many virtual NICs can connect to one virtual switch.
- VM-to-VM advice has to pass through the virtual switch.
- In this basic configuration, VM-to-server advice has to pass through a virtual switch and a physical switch.
VLANs
At the stage of creating a basic Hyper-V implementation, do not worry nigh setting upwardly a VLAN. A VLAN works to separate Layer 2 traffic and, at this stage, your main aim is to get physical and virtual Layer 2 devices to communicate. And so, working on separating out that traffic creates complexity.
If in that location are no VLANs on the physical network, you don't need them on your Hyper-Five hosts. If you lot utilise VLANs to dissever out Layer three traffic, you should design your Hyper-V hosts to match.
The utilise of VLANs is a major way that Hyper-V is different from VMWare ESXi. This is why y'all should clear your heed of everything you know about VMWare earlier implementing a Hyper-V project. The Hyper-V virtual switch automatically supports untagged frames and VLANs ane-4096 – this does non happen in ESXi. Too, Hyper-5 does not have a "default" VLAN designation, then don't worry about that. In Hyper-V, you fix VLANs on the virtual adapters, not on the virtual switch.
Basic Hyper-5 implementation goals
To summarize your aims when budgeted your commencement Hyper-V implementation:
- Get your Hyper-V management panel and all Hyper-5 services activated in your operating system.
- Convert a separate physical NIC on your physical server into a virtual switch
- Set up several VMs within the Hyper-5 environment.
- Connect your VMs to a physical switch on your network through your virtual switch.
Once those elements are all working and tin can communicate, yous take your bones Hyper-5 implementation working. Go familiar with the settings of that configuration and so advance to more complicated scenarios.
Activate Hyper-Five
Hyper-Five is integrated into Windows 10 and in Windows Server since version 2008 merely you have to activate it.
- In the taskbar search field type plow win and click to open Plow Windows features on or off
- Curl downwards in the popup that opens to find Hyper-V. Bank check the box next to it.
- Click OK.

After the organization processes the request, you lot volition be prompted to restart your computer.
Create a Virtual Switch
The virtual switch will support the VMs that y'all are going to create.
- Open Hyper-Five Manager.
- Select the Hyper-Five host computer name.
- Click on Action in the summit menu bar.
- In the driblet-down bill of fare, click on Virtual Switch Manager.
- In the Virtual Switch Managing director, click on New virtual network switch in the left panel.
- Cull a virtual switch type (External, Internal, or Private).
- Click on the Create Virtual Switch button. This opens up the Virtual Switch Properties panel.
- Give the virtual switch a proper noun and optionally type in a description. For example, Virtual switch for VMs.
- Optionally, change the type that you already specified by specifying the network to connect to. For an external network, you will need to specify the physical NIC to connect through.
- Click OK.
You will be shown a warning message that explains that the creation procedure will interfere with network activity. Click Yes to dismiss the message.
Create a Hyper-V Virtual Machine
You tin at present create a VM that will communicate through the virtual switch you just created.
A quick annotation on Generations, which is a concept that you will come across during the creation of the VM:
Generation ane
These VMs support 32-bit and 64-bit guest OSes and BIOS-based architecture. These are the original VM types of Hyper-V.
Generation 2
These VMs support 64-bit Windows OSs and the latest versions of Linux and FreeBSD OSes. They enable advanced features, such as Secure Boot.
The generation of a VM is fixed at the point of its creation and tin't exist changed afterwards.
Here'due south how to create a VM.
- Open Hyper-V Manager.
- Select the Hyper-V host reckoner proper name.
- Click on Action in the top menu bar.
- In the drib-downwards menu, expand New and click on Virtual Machine in the sub-menu. This opens the New Virtual Automobile Magician.
- Click Next on the opening page of the wizard.
- Name the VM and specify its location. You tin get out the location equally the path shown by default.
- Click on Next to accelerate to the Generation page.
- In the Generation section, choose between Generation 1 and Generation 2.
- Click on Next to become to the Assign Memory page.
- Bank check the Employ Dynamic Memory box on the memory page.
- Click on Next to advance to the Configure Networking page.
- The Configure Networking screen contains a drib-down listing of possible connections. The virtual switch you lot created should be in that list. Select it.
- Click on Next to get to the Virtual Hard Disk screen.
- Choose to create a new virtual hard disk drive, utilise an existing virtual hard disk drive, or skip this footstep and attach a virtual hard disk later.
- Click on Next to get to the terminal screen of the wizard.
- Wait through the settings summary and so click on Finish to create the VM.
If in step xiv, you cull to Create a Virtual Hard Disk, you lot need to make full out a supplementary screen, called Installation Options. You can defer this chore and and so movement out of the screen. If you make up one's mind to set the deejay upwardly at this point, yous demand to install an Bone on the disk. Your options are:
- Install the Bone from a CD-ROM
- Install the OS from a bootable floppy disk
- Install the OS from a network-based installation server
Teaming
There is a method available in later versions of Windows Server that would allow the virtual server to directly to the aforementioned virtual switch every bit the VM. This is a method, called teaming. It enables a grouping of network adapters to exist grouped together and provide i or more virtual switches.
If you employ teaming, you can manage all of the communications betwixt virtual servers and VMs within one concrete server. Withal, yous will still demand to loop out from the virtual switches to a physical switch in club to verify that the virtualization is able to piece of work beyond the network. Each virtual server or virtual auto connects to the virtual switch through a virtual NIC. The connexion through to a concrete switch is optional.
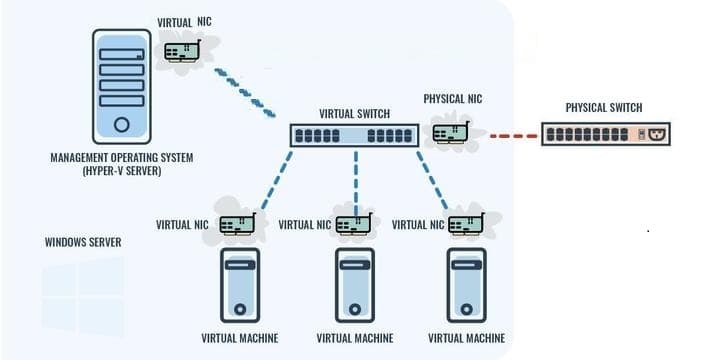
This configuration gives you options over the virtual switch style. In that location are three modes that you lot can use under this virtual setup:
- Private
- Internal
- External
Each of these options can be useful for enforcing or relaxing security and privacy.
Private Virtual Switch
A virtual switch in individual mode only allows communication between VMs connected to that virtual switch. This communication path is too possible in the basic setup of a Hyper-Five without teaming.

Internal Virtual Switch
This advice scenario is simply possible with NIC teaming. In reality, the communication between the VM and the server passes through two NICs, but the data exchange between those two adapters is obscured by the operating organisation service that manages the teaming operation. The Hyper-V virtual switch management system sits on top of the teaming service.

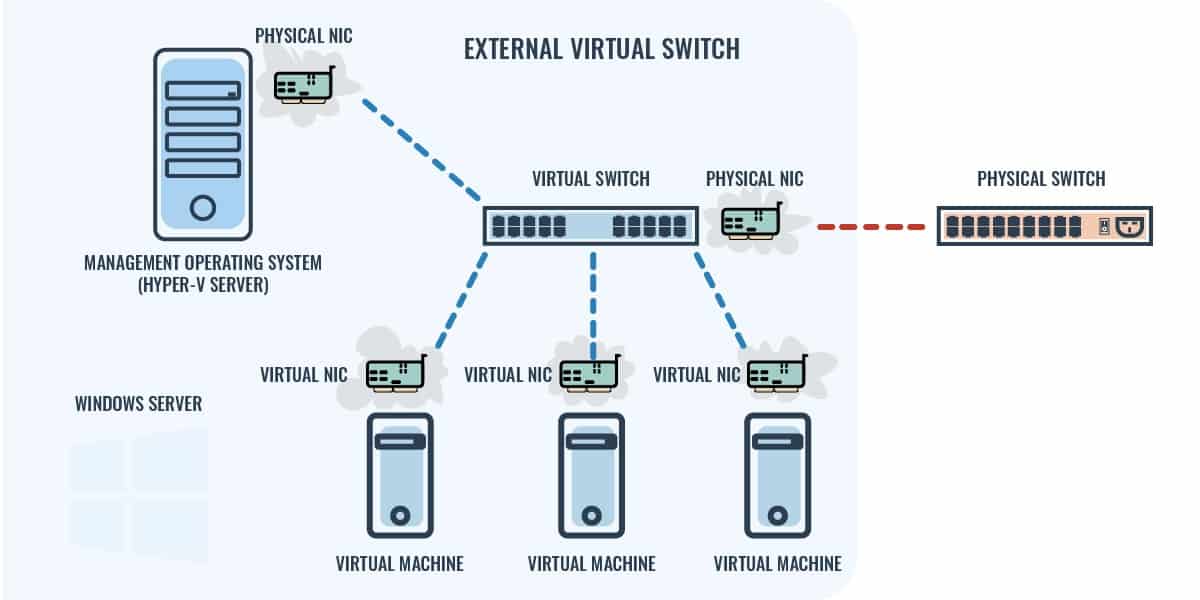
External Virtual Switch
This is the total virtual switch configuration that is enabled by teaming. In the basic configuration without teaming, the presence of a physical switch was necessary. In the teaming scenario, the physical switch is simply needed to communicate with other concrete devices across the network. Internal traffic is nonetheless possible and advice betwixt VMs or between each VM and a Hyper-V host is mediated by the virtual switch without the need for the physical switch to be involved. Equally with the internal fashion, communication between a VM and a Hyper-V server on the same host actually crosses ii physical NICs.
Virtual switches and PowerShell
You can create virtual switches through the Hyper-V management panel, but it is fourth dimension-consuming. Information technology is quicker to create and manage them in PowerShell. If yous are using teaming, you can manage that technique through PowerShell. There are also PowerShell cmdlets for creating and managing virtual NICs. You tin can also employ PowerShell to prepare a NIC squad.
A straightforward virtual NIC (not a team) is automatically created when you set a VM in the Hyper-V management console.
Create a team
In order for the same virtual switch to be for both a Hyper-V server and a VM, you lot demand to base it on at least two physical network adapters. In order to do this, you demand to create a Windows team of network adapters upon which you can create the virtual switch.
In club to meet all of the physical NIC that you take on your server, utilize the cmdlet Go-NetAdapter -Physical.
Notation down the names of two NICs. The proper name is the outset column in the output of Become-NetAdapter.
Apply the cmdlet New-NetLbfoTeam to create the team. Substitute the 2 NIC names yous noted for <NIC1> and <NIC2> in the post-obit command – don't leave the angle brackets in.
New-NetLbfoTeam -Name vNICGrp -TeamMembers <NIC1>, <NIC2> -TeamingMode SwitchIndependent -LoadBalancingAlgorithm Dynamic This creates a team NIC, a concept that is called "tNIC." The tNIC created by the above control is chosen vNICGrp, but you lot tin can call it any you like.
Here are some tNIC cmdlets that you might need to employ:
Get-NetLbfoTeam
Lists all tNICs
Get-NetLbfoTeamMember -Squad <team>
List all the NICs in <team>
Add-NetLbfoTeamMember -Proper noun <NIC> -Team <team>
Add <NIC> to <team>
Remove-NetLbfoTeamMember -Name <NIC> -Team <team>
Take <NIC> out of <team>
Create a Virtual Switch
You can turn a physical NIC into a virtual switch and you can also base a new virtual switch on a tNIC – the cmdlet is the same. Information technology is New-VMSwitch.
This creates an external virtual switch by default if the switch type is not specified. In the post-obit examples, the cmdlet creates a virtual switch chosen vSwitch based on the tNIC called vNICGrp.
To create an external virtual switch:
New-VMSwitch -Name vSwitch -NetAdapterName vNICGrp -AllowManagementOS $false -MinimumBandwidthMode Weight To create an internal virtual switch:
New-VMSwitch -Name vSwitch -NetAdapterName vNICGrp -SwitchType Internal -MinimumBandwidthMode Weight To create a individual virtual switch:
New-VMSwitch -Name vSwitch -NetAdapterName vNICGrp -SwitchType Private -MinimumBandwidthMode Weight Hither are some virtual switch management cmdlets that you lot might need:
Gear up-VMSwitch -Proper name <vswitch> -SwitchType Internal
Change a switch from external to internal
Fix-VMSwitch -Name <vswitch> -SwitchType Private
Change a switch from external to private
Set-VMSwitch -Name <vswitch> -NetAdapterName <vNICGrp>
Change a switch from private or internal to external
Set-VMSwitch -Name <vswitch> -NetAdapterName <vNICGrp2>
Movement a virtual switch to be based on <vNICGrp2> instead of its electric current tNIC
Remove-VMSwitch -Name <vswitch>
Delete virtual switch <vswitch>
Related post: Best Hyper-V Monitoring Tools
Source: https://www.comparitech.com/net-admin/hyper-v-networking-guide/
0 Response to "Can a Dual Nic Be Used for Two Seperate Excternal Private Hyperv Networks"
Publicar un comentario